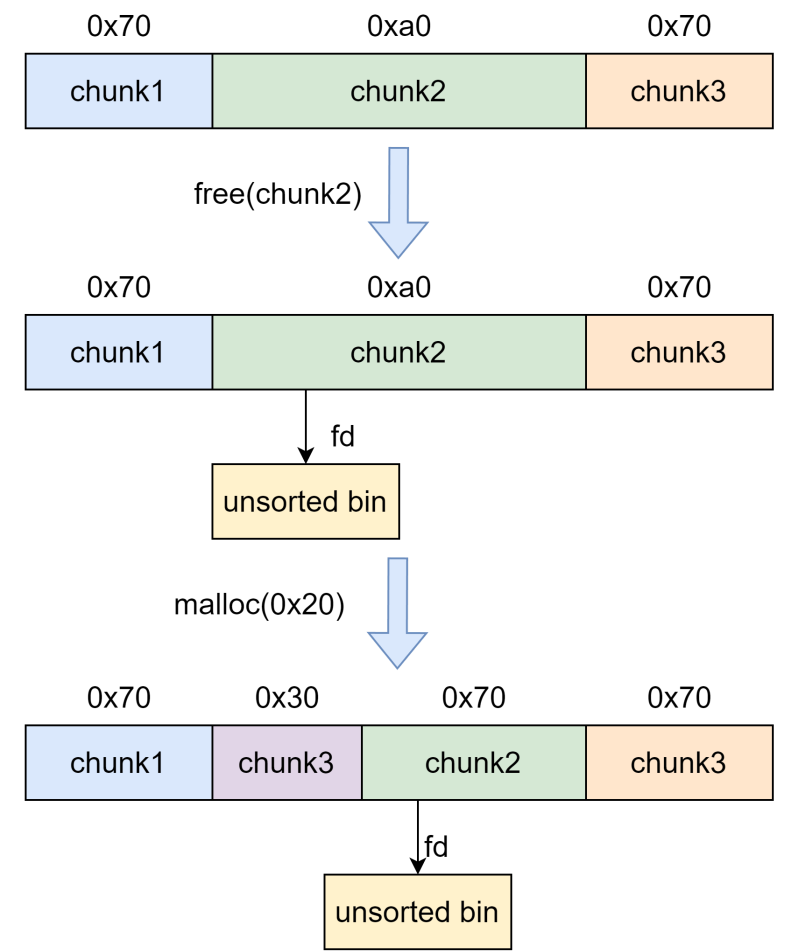
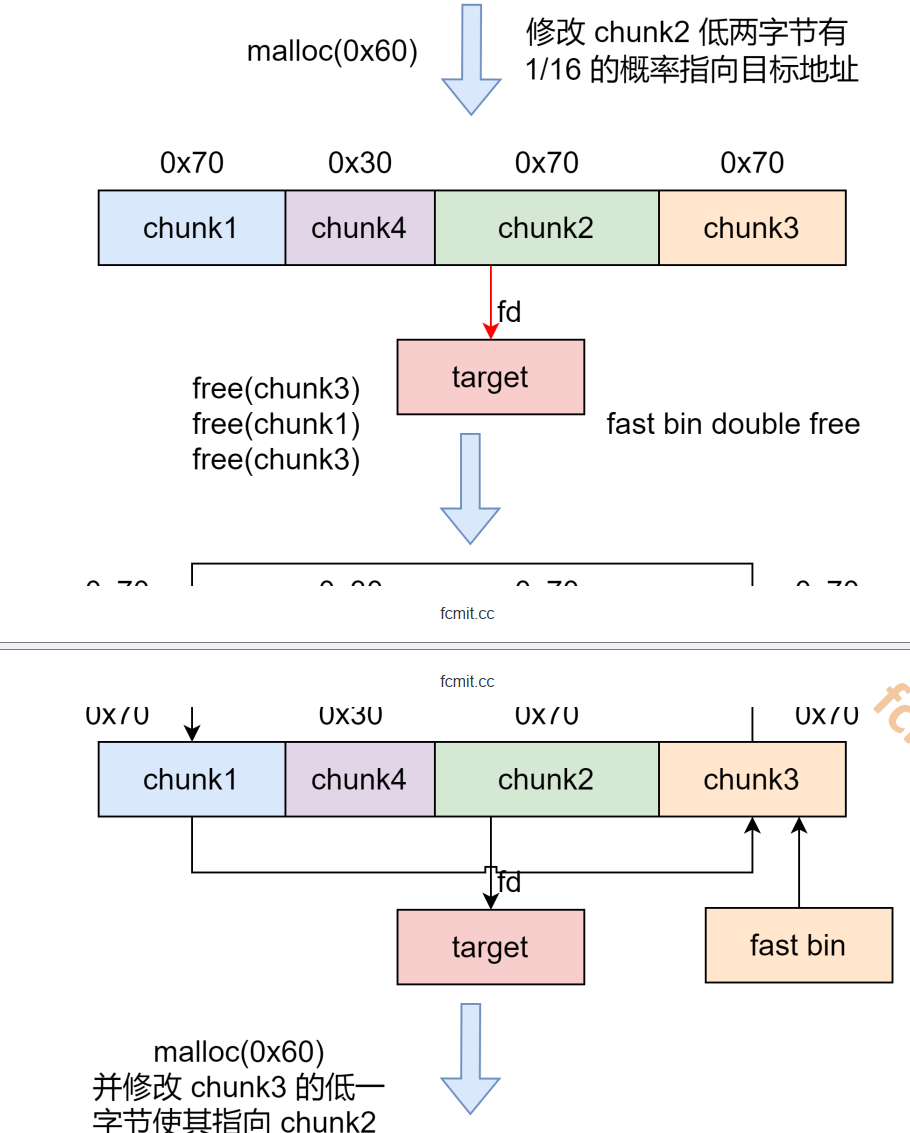
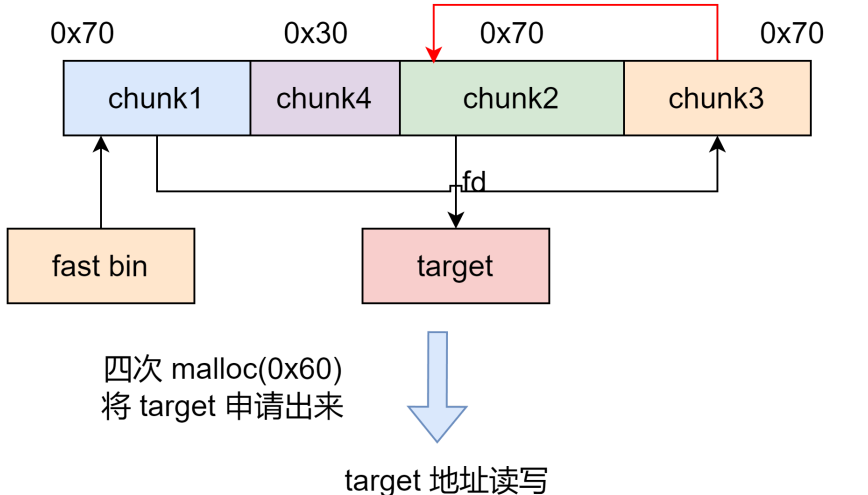
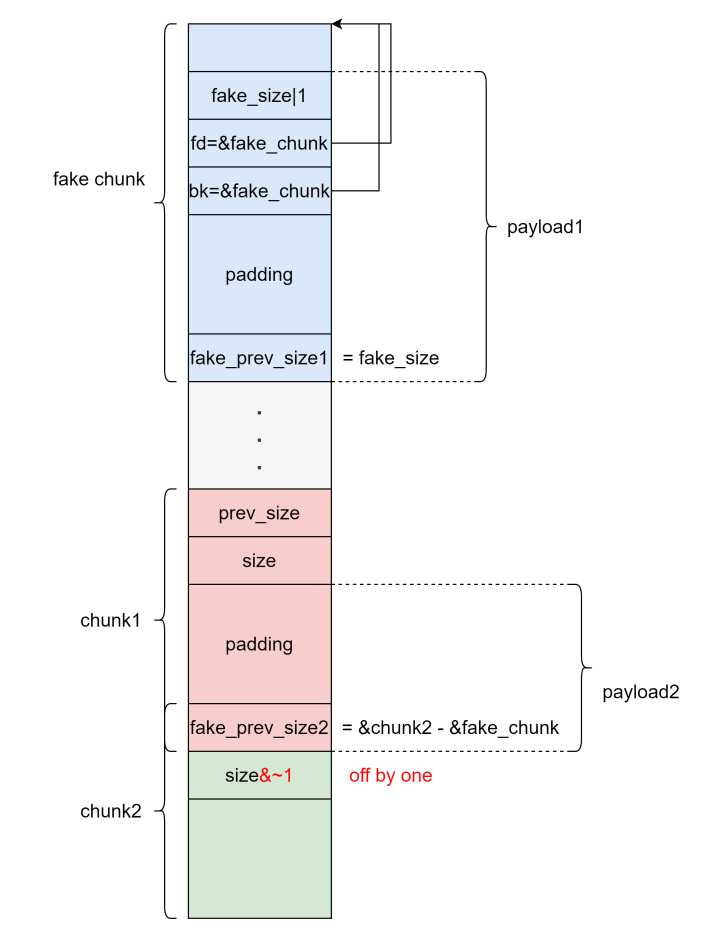
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
|
/* Copyright (C) 1993-2022 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This file is part of the GNU C Library.
The GNU C Library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
The GNU C Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
Lesser General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
License along with the GNU C Library; if not, see
<https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
As a special exception, if you link the code in this file with
files compiled with a GNU compiler to produce an executable,
that does not cause the resulting executable to be covered by
the GNU Lesser General Public License. This exception does not
however invalidate any other reasons why the executable file
might be covered by the GNU Lesser General Public License.
This exception applies to code released by its copyright holders
in files containing the exception. */
#include <libioP.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <shlib-compat.h>
static ssize_t
_IO_cookie_read (FILE *fp, void *buf, ssize_t size)
{
struct _IO_cookie_file *cfile = (struct _IO_cookie_file *) fp;
cookie_read_function_t *read_cb = cfile->__io_functions.read;
#ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE
PTR_DEMANGLE (read_cb);
#endif
if (read_cb == NULL)
return -1;
return read_cb (cfile->__cookie, buf, size);
}
static ssize_t
_IO_cookie_write (FILE *fp, const void *buf, ssize_t size)
{
struct _IO_cookie_file *cfile = (struct _IO_cookie_file *) fp;
cookie_write_function_t *write_cb = cfile->__io_functions.write;
#ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE
PTR_DEMANGLE (write_cb);
#endif
if (write_cb == NULL)
{
fp->_flags |= _IO_ERR_SEEN;
return 0;
}
ssize_t n = write_cb (cfile->__cookie, buf, size);
if (n < size)
fp->_flags |= _IO_ERR_SEEN;
return n;
}
static off64_t
_IO_cookie_seek (FILE *fp, off64_t offset, int dir)
{
struct _IO_cookie_file *cfile = (struct _IO_cookie_file *) fp;
cookie_seek_function_t *seek_cb = cfile->__io_functions.seek;
#ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE
PTR_DEMANGLE (seek_cb);
#endif
return ((seek_cb == NULL
|| (seek_cb (cfile->__cookie, &offset, dir)
== -1)
|| offset == (off64_t) -1)
? _IO_pos_BAD : offset);
}
static int
_IO_cookie_close (FILE *fp)
{
struct _IO_cookie_file *cfile = (struct _IO_cookie_file *) fp;
cookie_close_function_t *close_cb = cfile->__io_functions.close;
#ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE
PTR_DEMANGLE (close_cb);
#endif
if (close_cb == NULL)
return 0;
return close_cb (cfile->__cookie);
}
static off64_t
_IO_cookie_seekoff (FILE *fp, off64_t offset, int dir, int mode)
{
/* We must force the fileops code to always use seek to determine
the position. */
fp->_offset = _IO_pos_BAD;
return _IO_file_seekoff (fp, offset, dir, mode);
}
static const struct _IO_jump_t _IO_cookie_jumps libio_vtable = {
JUMP_INIT_DUMMY,
JUMP_INIT(finish, _IO_file_finish),
JUMP_INIT(overflow, _IO_file_overflow),
JUMP_INIT(underflow, _IO_file_underflow),
JUMP_INIT(uflow, _IO_default_uflow),
JUMP_INIT(pbackfail, _IO_default_pbackfail),
JUMP_INIT(xsputn, _IO_file_xsputn),
JUMP_INIT(xsgetn, _IO_default_xsgetn),
JUMP_INIT(seekoff, _IO_cookie_seekoff),
JUMP_INIT(seekpos, _IO_default_seekpos),
JUMP_INIT(setbuf, _IO_file_setbuf),
JUMP_INIT(sync, _IO_file_sync),
JUMP_INIT(doallocate, _IO_file_doallocate),
JUMP_INIT(read, _IO_cookie_read),
JUMP_INIT(write, _IO_cookie_write),
JUMP_INIT(seek, _IO_cookie_seek),
JUMP_INIT(close, _IO_cookie_close),
JUMP_INIT(stat, _IO_default_stat),
JUMP_INIT(showmanyc, _IO_default_showmanyc),
JUMP_INIT(imbue, _IO_default_imbue),
};
/* Copy the callbacks from SOURCE to *TARGET, with pointer
mangling. */
static void
set_callbacks (cookie_io_functions_t *target,
cookie_io_functions_t source)
{
#ifdef PTR_MANGLE
PTR_MANGLE (source.read);
PTR_MANGLE (source.write);
PTR_MANGLE (source.seek);
PTR_MANGLE (source.close);
#endif
*target = source;
}
void
_IO_cookie_init (struct _IO_cookie_file *cfile, int read_write,
void *cookie, cookie_io_functions_t io_functions)
{
_IO_init_internal (&cfile->__fp.file, 0);
_IO_JUMPS (&cfile->__fp) = &_IO_cookie_jumps;
cfile->__cookie = cookie;
set_callbacks (&cfile->__io_functions, io_functions);
_IO_new_file_init_internal (&cfile->__fp);
_IO_mask_flags (&cfile->__fp.file, read_write,
_IO_NO_READS+_IO_NO_WRITES+_IO_IS_APPENDING);
cfile->__fp.file._flags2 |= _IO_FLAGS2_NEED_LOCK;
/* We use a negative number different from -1 for _fileno to mark that
this special stream is not associated with a real file, but still has
to be treated as such. */
cfile->__fp.file._fileno = -2;
}
FILE *
_IO_fopencookie (void *cookie, const char *mode,
cookie_io_functions_t io_functions)
{
int read_write;
struct locked_FILE
{
struct _IO_cookie_file cfile;
#ifdef _IO_MTSAFE_IO
_IO_lock_t lock;
#endif
} *new_f;
switch (*mode++)
{
case 'r':
read_write = _IO_NO_WRITES;
break;
case 'w':
read_write = _IO_NO_READS;
break;
case 'a':
read_write = _IO_NO_READS|_IO_IS_APPENDING;
break;
default:
__set_errno (EINVAL);
return NULL;
}
if (mode[0] == '+' || (mode[0] == 'b' && mode[1] == '+'))
read_write &= _IO_IS_APPENDING;
new_f = (struct locked_FILE *) malloc (sizeof (struct locked_FILE));
if (new_f == NULL)
return NULL;
#ifdef _IO_MTSAFE_IO
new_f->cfile.__fp.file._lock = &new_f->lock;
#endif
_IO_cookie_init (&new_f->cfile, read_write, cookie, io_functions);
return (FILE *) &new_f->cfile.__fp;
}
versioned_symbol (libc, _IO_fopencookie, fopencookie, GLIBC_2_2);
#if SHLIB_COMPAT (libc, GLIBC_2_0, GLIBC_2_2)
static off64_t
attribute_compat_text_section
_IO_old_cookie_seek (FILE *fp, off64_t offset, int dir)
{
struct _IO_cookie_file *cfile = (struct _IO_cookie_file *) fp;
int (*seek_cb) (FILE *, off_t, int)
= (int (*) (FILE *, off_t, int)) cfile->__io_functions.seek;
#ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE
PTR_DEMANGLE (seek_cb);
#endif
if (seek_cb == NULL)
return _IO_pos_BAD;
int ret = seek_cb (cfile->__cookie, offset, dir);
return (ret == -1) ? _IO_pos_BAD : ret;
}
static const struct _IO_jump_t _IO_old_cookie_jumps libio_vtable = {
JUMP_INIT_DUMMY,
JUMP_INIT(finish, _IO_file_finish),
JUMP_INIT(overflow, _IO_file_overflow),
JUMP_INIT(underflow, _IO_file_underflow),
JUMP_INIT(uflow, _IO_default_uflow),
JUMP_INIT(pbackfail, _IO_default_pbackfail),
JUMP_INIT(xsputn, _IO_file_xsputn),
JUMP_INIT(xsgetn, _IO_default_xsgetn),
JUMP_INIT(seekoff, _IO_cookie_seekoff),
JUMP_INIT(seekpos, _IO_default_seekpos),
JUMP_INIT(setbuf, _IO_file_setbuf),
JUMP_INIT(sync, _IO_file_sync),
JUMP_INIT(doallocate, _IO_file_doallocate),
JUMP_INIT(read, _IO_cookie_read),
JUMP_INIT(write, _IO_cookie_write),
JUMP_INIT(seek, _IO_old_cookie_seek),
JUMP_INIT(close, _IO_cookie_close),
JUMP_INIT(stat, _IO_default_stat),
JUMP_INIT(showmanyc, _IO_default_showmanyc),
JUMP_INIT(imbue, _IO_default_imbue),
};
FILE *
attribute_compat_text_section
_IO_old_fopencookie (void *cookie, const char *mode,
cookie_io_functions_t io_functions)
{
FILE *ret;
ret = _IO_fopencookie (cookie, mode, io_functions);
if (ret != NULL)
_IO_JUMPS_FILE_plus (ret) = &_IO_old_cookie_jumps;
return ret;
}
compat_symbol (libc, _IO_old_fopencookie, fopencookie, GLIBC_2_0);
#endif
|